FAMILY PLANNING
Family planning is a family health and welfare.
A WHO expert committee in 1971 defined and described family plannning as follows:
 “Family planning refers to the practices that helps the individual and couples to attain certain objectives” as follows
“Family planning refers to the practices that helps the individual and couples to attain certain objectives” as follows
Objectives of family planning
i. To avoid the unwanted pregnanacy
ii. To bring about the wanted births
iii. To regulates the intervals between pregnancies
iv. To control the time at which birth occurs in relation to the age of the parents
v. To determine the number of children in the family
It has been defined by WHO (1971) as “Family planning is the way of thinking and living that is adopted voluntarily ,upon the basis of knowledge,attitude and responsible decisions by individuals and couples in order to promote the health and welfare of the family group and thus contribute effectively to the social development of the country.”
Services that makes these practices possible includes
i. Education and counselling on family planning
ii. The provision of contraceptives
iii. The management of infertility
iv. Education about sex and parenthood
v. Organisationally related activities such as genetic and marriage counselling ,screening for malignancy and adoptation services
Scope of family planning services:
Family planning is a basic human right (UNO 1968).All couples and individuals have the basic human right to decide freely and responsible on the number and spacing of their children and to have the information ,education and mean to do so.The modern concept of family planning ,not synonomus with the birth control includes and extends the following
i. The proper spacing and limitation of the birth
ii. Advice on sterility
iii. Eduation about parenthood
iv. Sex education
v. Screening for pathological conditions related to the reproductive system
vi. Genetic counselling
vii. Premarital consultation and examination
viii. Carry out pregnacy test
ix. Marriage counselling
x. The preparation of the couples for the arrival of first child
xi. Providing services for unmarried mother
xii. Teaching home economics
xiii. Providing adoption services
CONTRACEPTIVE METHODS:
Contraceptive methods are by definition; preventive methods to help women to avoid unwanted pregnancies.They include all temporary and permanent measures to prevent pregnancy resulting from coitus.
The contraceptives methods may be boardly grouped into two classes
Spacing methods and terminal methods as shown below
A. Spacing methods:
1. Behavioural /natural methods
i. Lactational ammenorrhoea method(LAM)
ii. Calender method
iii. Cervical mucous method
iv. Temperature method
v. Withdrawl method
2. Chemical methods
i. Spermicides (foams tablet/kamal)
ii. Jelly ,paste and cream
3. Mechanical methods
I. Condom –male condom
-female condom
-female condom
II. IUCD
III. Diaphragm
IV. Cervical cap
4. Hormonal methods or physiological methods
i. Combined oral pills
ii. Depoprovera
iii. Norplant
B. Terminal methods:
1. Male sterilization
2. Female sterilization
A. SPACING METHODS:
1. Behavioural /natural methods:
I. Lactational ammenorrhoea method(LAM):
 LAM is the use of breatfeeding as a temporary family planning method.It is believed that there is a higher probability that the women who is amenorrhoeal while breast feeding will be able to regulates her fertility in first 6 month post partum even if she introduces supplementation in the baby’s feeding.When a baby sucks from the mother’s breast,there is reflux release of prolactin from the pituatary which acts to prevent ovulation.It isnot fixed when menstruation and ovulation occurs.Some women may ovulate before menstruation so,they need to use another method of family planning except oral pills.
LAM is the use of breatfeeding as a temporary family planning method.It is believed that there is a higher probability that the women who is amenorrhoeal while breast feeding will be able to regulates her fertility in first 6 month post partum even if she introduces supplementation in the baby’s feeding.When a baby sucks from the mother’s breast,there is reflux release of prolactin from the pituatary which acts to prevent ovulation.It isnot fixed when menstruation and ovulation occurs.Some women may ovulate before menstruation so,they need to use another method of family planning except oral pills.
Effectiveness is as commonly used 2 pregnancies per 100 women in the first 7 months after child birth (1 in every 50)
Advantages:
· Effectively prevents pregnancy for at least 7 months and may be longer if a mother keeps breastfeeding often days and night
· Encourages the best breast feeding patterns
· Can be used immediately after child birth
· No need to do anything at the time of sexual intercourse
· No supplied or procedure needed to prevent pregnancy free from side effects
· Promotes male involvemetn communication as a couple
· Can be taught by trained non medical personnel
· Available and easy to use
· No hormonal side effects
Disadvantages:
· Effectiveness after 7 month is not certain
· Frequent breastfeeding may be inconvinent or difficult for some women especially working women
· No protection against STI including HIV/AIDS
· Both partner must be commited and cooperative
· If the mother has HIV there is a small chance that breast milk will pass HIV to the baby
Instruction to the client:
· Breastfeeding should be encouraged i.e demand feeding generally 6-10 times per day; every 4 hours on day and every 6 hours on night.
· Once the menstrual period return, the client is more likely to fertile then.
· Always keep the back up method of contraception such as condoms readily available,use it if her baby is 6 months old ,her menses returns or she begins to supplement her baby’s diet
· then return to the clinic for long term method of desired (IUD,Norplant,Depo-provera,COCs)
II. Safe period/rhytm method(calender method):
· Ovulation occurs on 14th day(13 to 16 days) of menstrual cycle
· The life of ovum is generally not more than 2 days
· The life of sperm is not more than 3 days,If these risk days are avoided the chances of pregnancy will be reduced by nearly 80%
· In 28 days of menstrual cycle from 11-18 days is the unsafe period but every women has a different cycle
III. Cervical mucous method:
It is the first stage of the cervical mucousa is little and thick.During ovulation(when ovum comes out from ovaries)the amount of cervical mucus increased .It is watery,slippery between the tips of the finger.The cervical mucous is much watery ,and can form a thread .The couples use a barrier method until 3 days.
IV. Temperature method
A women’s body temperature goes up slightly around time of ovulation (relaease of egg).women should measure early in the morning before getting up from the bed, keep the thermometer in the mouth for 1-5 minute, since the temperature rises slightly after the ovulation, the average temperature between 0.2-0.4°C.If the temperature slightly rises, abstain from sex for 3 days.This method is not suitable .Failure rate is higher
.
V. Withdrawl method(coitus interrupts)
This method is voluntarily fertility involves no cost or appliance.It continues to be widely practices method.The male withdrawl before the ejaculation and thereby tries to prevent deposition of seen in vagina.Some couples are able to practise this method sucessfully.The chief drawback of this method is that the pre ciotal secretion of the male may contain sperm, and even a drop of semen is sufficient for pregnancy .Futher ,the slightest mistake in timing the withdrawl may lead to the deposition of a certain amount of semen .Therefore the failure rate with this method may be high a 25%.
A man who performs withdrawl will pull his penis out of the vagina before ejaculation, the moment when semen spurts out of his penis .Withdrawl is also known as coitus interrupts and the pull out method.
Withdrawl may be the world oldest way to practise birthcontrol.About 35 million couples worldwode rely on withdrawl.
Mechanism of action:
Withdrawl prevents the pregnancy by keeping sperm out of the vagina.Pregnancy cannot happen if there is absence of sperm.
Effective:
Effectiveness is an important and common concern when choosing a birth control method.Like all birth control methods; the pullout method is much more effective when it is done correctly
Of every 100 women whose partners use withdrawl, 4 will become pregnant each year if they do it correctly.
Of every 100 women whose partner use withdrawl, 27 will become pregnant each year if they don’t always do it correctly
Couples who have great self control, experience and trust may use the pull out methodmore effectively.
2. Chemical methods
I. Spermicides (foam tablet/kamal)
Foam tablet (kamal) partly acts as a physical barrier to the sperm and partly as spermicidal.Moisten one or two tablets with clean water.Insert deep into the vagina, 5 to 30 minutes before sexual intercourse.Let the tablet dissolve.The dissolved tablets create a barier by immobilizing the sperms and preventing them from going up in the cervix
Advantages of foam tablets:
· Cheap,safe and harmless
· Easy to use and easily available in the market
· Donot affect health
· Donot need from any medical personnel
· Prevents vaginal disease
Drawbacks of foam tablets:
· A short period available between insertion and use
· The tablet may not dissole properly if the vagina is dry
· The tablet may cause irritation or burning in the presence of cervicitis or vaginitis
· The tablets spoil soon when left in the open
II. Jelly ,paste and cream:
These jelly paste and creams are also introduced into the vagina bya special applicator ,3 to 4 minutes before the sexual intercourse.At body temperature they spread in the vagina.they are spermicidal.Cream and jelly are highly effective in combination with mechanical contraceptives .If they cause burning or irritation they should not be used.
3. Mechanical methods
I. Condom –
a) Male condom:
Condom (nirodh, dhal) is the most widely used contraceptive device for males.It is made of synthetic rubber.It gives greater protection when combined with spermicides.
· Easy to use,cheap and harmless
· Easily available in market
· Protects from veneral disease
· No side effects
Drawkbacks of barrier method
· May brust ,tear or slip off during use
· Burning and uneasy feeling at the beginning of use
Client’s instructions:
· Use a condom every time you have intercourse
· Use spermicide with the condom for maximum effectiveness and protection
· Do not use teeth,knife or sharp instrument to open the package
· The condom should be unrolled on to the erect penis before the penis enters the vagina because the pre ejacualtory semen contains active sperm
· If the condom doesn’t have an enlarged end(reservior tip) about 1-2 cm should be left at the tip for the ejaculation
· While holding on to the base (ring) of the condom,withdraw the penis before losing the erection,this prevents the condom from spilling semen
· Each condom should be used only once
· Donot use lubricates such as mineral oils,cooking oil.baby oil with the condom.they cause the detoriation of condom may break.If lubricant required vaginal secretion or kamal spermicide
· Supplies of condoms are available for through FCHVs, subhealth post, health posts, family planning clinics.
· If condom breaks ,replace immediately
b) Female condom(diaphragm)
It is the mechanical barrier made uo of synthethic rubber.Its diameter ranges in size from about 5 to 10 cms (2 to 4 inches).It stops sperms from getting into the cervical canal.The diaphragm is inserted before the sexual intercourse and must remain in place for at least 6 hours after the intercourse.It can be left in place for 24 hours without any discomfort.
After using the diaphragm, one should clean it and keep in a dry place for use next time.Donot use the diaphragn if the uterus is prolapsed.
· Not expensive
· may last for a considerable period if it is used properly
Drawbacks of the method:
· Doctor or nurse is required to fit it
· It is difficult to teach women to use it(especially in rural areas)
Cervical cap is smaller than diaphragm.It is made up of synthethic rubber .It is available in different sizes. So, women need to select the right size, Donot keep the cervical cap inside the body for more than 3 days.It may cause infection; after using clean it and keep it in dry, safe place.It can be used next time.The cervical cap is difficult to use and may cause friction during intercourse.Don’t use if the uterus is prolapsed.
Vaginal sponge is round in shape .It has a thread for easy removal.It is wet in water before use.Wetting it activates the spermicidal action.The vaginal sponge may be inserted 24 hours before the intercourse-it works for 24 hours.It should be kept in place at least 6 hours after the intercourseTthe vaginal sponge is spermicidal; it absorbs sperms and stops them from entering cervical canal.
Advantages of vaginal sponge
· No bad effect to health
· Easy to use(with out any health worker)
· No discomfort
· Can be placed 24 hour before the intercourse
· Available only in one size so no need to decide on size
Drawbacks of vaginal sponge:
Not very reliable: according to study, 9-27% women were found pregnant in the first year (the study of effectiveness was not complete)
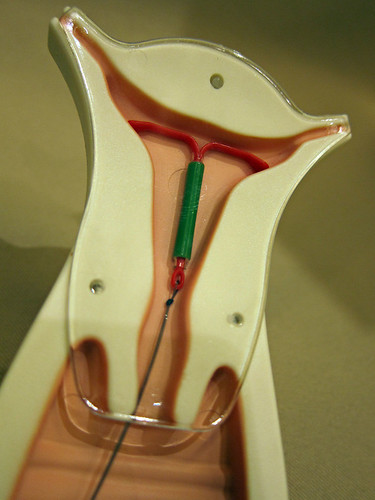
II. IUCD(intrauterine contraceptive device)/IUD:
Intrauterine contraceptive device is method of controlling conception by introducing foriegn body into the uterus.The effectiveness of IUD is 99.2%
The IUD TCU 380A was recently approved for 12 years.the copper 380A is “T”shaped and has a copper notch stem and arms, with a total exposed copper area of 380 sq.mm.
I.Non medicated (first generation IUD): usually made of polyethlene or polymers.eg.Loop, spiral, coils rings
ii.Medicated (second generation IUD): Comprises of copper in IUDs.It is found that metallic copper has strong anti fertility effect, eg.copper-7, copperT-200, and copperT-380A
iii. Hormone releasing (third generation): Based on pronciple of release of a hormone .The most widely used hormonal device is project osert, which is a t shaped device filled with progesterone.The hormone is released slowly at the rate of 65 mcg daily.
Mechanism of action:
· IUD prevents fertilization of the ovum and decrease the number of sperm reachin the fallopian tube
· It is produce other local effects that may contribute to their contraceptive action.Copper seems to enhance the cellular response in the endometrium.It also assects the enzymes in the uterus.By altering the biochemical composition of cervical mucus,copper ions may affect sperm motility capacitating and survival
· Hormone releasing devices increase the viscosity of the cervical mucus and there by prevent from entering the cervix.They also maintain high level of progesterone in the endometrium and thus ,relatively low level of estrogen there by sustaining an endometrium unfavourable to implantation.
Advantages:
· Highly effective
· Effective immediately
· Immediately return to fertility after removal
· Few side effects
· Do not interfere with intercourse
· Convinent
· No supplies neede by the client
· Do not affect in breast feeding
· Long term method(upto 12 years protection copper T380A)
· After follow up visit client need to return to clinic only if problem arises
Disadvantages:
· Pelvic examination required and screeining for genital tract infection (GTIs) recommended before insertion
· Required trained personnel to insertion and removal
· Need to check for strings if necessary
· Increase menstrual bleeding and cramping during first few month of use
· Women cannot stop use whenever she wants
· May increase the risk of PID and subsequent risk of GTIs and other STIs(e.g.HBV,HIV/AIDS)
· May be spontaneously expelled
Indications:
The women who are:
· Of Any Reproductive age
· No sign and symptoms of pregnancy or
· Breastfeeding and need contraception
· Postpartum and breast feeding
· Post abortion
· Women at low risk of GTIs and other STIs
· Shouldnot hormonal methods
Contraindications:
· Known pregnancy
· Active or recurrent pelvic infection
· Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding
· Cancer of cervix,uterus and pelvic tumour
· Previous ectopic pregnancy
· Postpartum endometriosis
· Acute cervicitis
· Anaemia
· menorrhagia
Precautions:
· Suspected pregnancy
· Pelvic inflammation disease
· Unexplained vaginal bleeding
· Simple vaginal infection
· Painful menstrual bleeding
4. Hormonal methods or physiological methods
A. Combined Oral Contraceptives(COCS)
The combined oral contraceptives (COCs) pill is the one of the most reliable reversible methods that can be provided beyond the health service where most people of Nepal reside.
Combined oral pills are considered as a very reliable method of contraception.All combined COCs contain the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
Estrogen in the pills usually prevents release of eggs, progesterone cause thick and scanty cervical mucus to prevent sperm travelling into the uterus
Types of combined oral contraceptives (COCs)
In Nepal, the most commom COCs are low dose pills in 28 days package.Therefore, there names and composition are as follows
a. Gulf:It contains menstranel (oestrogen)50 mcg and northidrone(progesterone) 1 mg the brownish tablet contain 75 mg of ferrous sulphate
b. N ilocan:It contains ethinyl oestradiol 35 microgram and northindrone 0.5mg.Porgesterone is less so the side effect are less in nilocan
c. Lo-femanal:Available at all HMG facilities which contains norgestral(progestin)0.3mg and ethyinyl estradial (estrogen)
d. Sequential estrogen :It is given alone for 14 to 16 days beginning on the 5th day of menstrual cycle and followed by a tablet containing esrogen and progesterone during the next 5 to 7 days
e. Micro pills(progesterone only):They are given in a low dose for 30 days even during menstruation.A small dose of progesterone doesn’t interfere with pituatory hypothalamic ovarian functions
Advantages:
· Very effective with correct use(<1 pregancy per 100woman -years)
· Donot interfere with intercourse
· Easy to discontinue at any time
· Non contraceptive health benefits
· Available at health facilities and medical shops
· Doesn’t require pelvic examination to use few method related side effects
· Low cost
· Makes menstrusl regular and cure dysmenorrhoea
Disadvantages:
· Must be used correctly to be most effectively
· Requires daily/correct use and regular resupply
· Less appropriate while breast feeding
· Donot prevent from STI/HIV/AIDS,HBV
· Some during interactions(rifampicin for TB medications for seizure disorders)
· Minor side effects like ammenorrhoea,spotting between periods,irregular heavy bleding,breast tenderess,weight gain,nausea,headache
Contraindications:
· Severe hypertension
· Venous thrombosis
· History of cholestatic jaundice in pregnancy
· Confirmed pregnancy
· Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding
Precautions:
· Suspected pregnancy
· Jaundice
· Heavy smoking or age above 35 years
· Migraine headache with focal neurological symptoms
· Current or suspected breast cancer
· Breastfeeding less than 4 months post partum
· Long term use of anticonvulsants and rifampicin
When to start COCs:
The women who has:
· No sign and symptoms of pregnancy or
· No intercourse since last menses
· Correct or consistent use of relaible method or
· Within 6 week postpartum(non breast feeding) or
· Within 4 month post partum(breastfeeding)
· Within 7 days post abortion or immediately
Instruction for the use of COCs:
Start the pill in the top left hand corner of the packet and continue taking the next pill one day each,until the white packet is gone(for 21 days) and then start the brown pills taking 1 pill each day for 7 days untill all are gone.No rest period.
When the 28 days packet is empty, she should start taking pills from a new packet the next day.She should take the pill at bed time or with the evening meal.
Mild side effects are normal but in case of severe adominal and pelvic pain, severe chest pain and shortness of breath, headache, vision loss, severe leg cramps; she should come back to clinic.
In case of missed pills,
If she forgets 1 pills.Take as soon as she remembers, continue packet of pills as usual.
If she forgets 2 or more pills.Take 2 pill a day until she catch up-continue packet of pills as usual
Use back of method condoms or not have sex for 7 days.
B. Depoprovera:
The only injectable contraceptive available in Nepal is depot-medroxy progesterone acetate or DMPA.
 It is commonly called “Depo”, “Sangini”, “tin mahiney Sui”.It comes in a single dose vial containing 150 mg (1ml)
It is commonly called “Depo”, “Sangini”, “tin mahiney Sui”.It comes in a single dose vial containing 150 mg (1ml)
It helps in supressing ovulation, reducing sperm transport in upper genital tract (fallopian tubes), change endometrium making implantation less likely and thickening cervical mucus.
Advantages:
· Highly effective (99%)
· Rapidly effective(<24 hours)
· Easy to use
· Can provide long term protection
· Pelvic exam is not required to begin the use
· Few method related health risk since there is no estrogen
· Doesn’t interfere in sexual desire
· Convinent:only action required of used is to go for her injection every 3 month
· No supplies needed to client
· Effectiveness continues even if the client is upto 2 weeks late for her return visit
· Does no adversely affect on breast feeding
· Reversible
· Easily administered by a non physician
· Can be used by older women(over 40)
· Useful for women who want no more children,but prefer not to have sterilization
· May be used by post abortion clients
Disadvantages:
· Doesnot protect against most STI including HIV/AIDS
· Causes menstrual changes in most users
· Amenorrhoea in 50 -80% of users
· Irregular bleeding including spotting
· Possibly delay in return to fertility after discontinuation
· Must return to the health post for injections or attend a DMPA mobile outreach clinic if possible
· Client cannot discontinue the method on her own before next injection
· Weight gain as a common side effect(may not be a disadvantage for many clients)
· May cause depression
· Side effects of prolong bleeding or no bleeding at all;headache ,dizziness,breast tenderness or discomfort
Time of injection:
Optimal time for giving the injection is:
· During menstruation:within seven days of onset
· Post abortion:immediately or within the first seven days
· Post partum:when post partum mother brings her infant for immunizations(6 week postpartum)
· If fully breast feeding amenorrhoea and less than 6 month postpartum(LAM).The first injection can be delayed until her baby is 6 month old ,her menses returns or she begins to supplement her baby’s diet
Indications:
Women of any reproductive age or parity who
· Desire effective reversible method
· Cannot take estrogen
· Are breast feeding(6 weeks or more postpartum)
· Are post abortion
· Do not mind irregular bleeing or amenorrhoea
Contraindications:
· The only absolute contraindication of DMPA is known or confirmed pregnancy
Precautions:
· Suspected pregnancy
· Unexplained vaginal bleeding
· Active liver disease or liver tumours
· Breast lumps or suspected breat cancer
· Diabetes
· Depression
· Women unable to accept change in their menstrual cycle
Instructions:
She should return to the health centre for another injection every 12 weeks.However, next DMPA injection can be given up to 2 weeks before and after her appointment date.
Note: If the client comes after 14 weeks from her last injection,donot give DMPA injection unless she is currently menstruating or is in the first 7 days of her cycle or if you can be reasonably aure she is not pregnant.Give condoms and instruct the woman to return when she next menstruation.
Instruct the client to return immediately if:
· Heavy bleeding twice as long or twice as much bleeding between periods for more than 7 days
· Delayed menstrual period after a long interval of regular period
C. Norplant :
The sub dermal implants are the new generation of long acting contraceptives. Norplant implants are the registered trademark of the population council for contraceptive subdermal implant.
Norplant are usually placed under the skin on the inside of a woman’s upper arm in a fan shaped figuration using a simple trocar under local anaesthesia via minor surgical procedure. The norplant contain levonorgestrol progesterone hormone slowly diffuse through 6 slender,flexible capsules.Each of the stick is 34 mm long ,with a diameter of 2.4 mm.The 36 mg of levonorgestrel of six capsules is released at a slow steady rate of about 50 mcg per day by a month.The hormone release radually declines ta about 35 mcg per day at 18 months.Followed by a further decline to a steady level of 30mcg/day till the remaining time.It is recommended that norpalnt implants be replaced after 7 years.
Norplant is one of the most effective contraceptive methods; the average annual pregnancy rate for norplant is less than 1%.
Mechanism of action:
· Supress ovulation
· Decrease tubal mobility
· Change endometrium
· Thicken cervical mucus
Timing of insertion:
· During menstruation:within seven days of onset
· Post abortion:immediately or within the first seven days
· Post partum:when post partum mother brings her infant for immunizations(6 week postpartum)
· If fully breast feeding amenorrhoea and less than 6 month postpartum(LAM).the insertion can be delayed until her baby is 6 months postpartum
Advantages:
· Highly a rapidlyffective,continious method lasting up to 7 years
· Safe easy to use and doesnot interfere with intercourse or sexual desire
· Immediate return to previous level of fertility
· Doesnot interfere with breastfeeding
· Comfortable and obtrusive
· Pelvic exam not required
· Few method- realted health risks because it contains no estrogen
· No supplies needed by client
· Reversible
· Can be removed any time for any reasons
Disadvantages:
· Menstrual changes very common
· Weight gain or loss may occur
· Requires surgical insertion and removal
· No protection STI/HIV/AIDS
· Possible visibility of implants
· Other Side effects like:headche nausea, vomitting, nervousness, breast tenderness, depression, chest pain, hyperpigmentation over implant site, galactorrhoea, appetite changes, and change in blood pressure
Indications:
Woman who
· Want long term birth spacing
· Want no more children but are not ready for sterilization
· Are postpatrum(after 6 weeks if breastfeeding)
· Post abortion clients
· Have sucessfully used other progesterone only methods
· Do not mind irregular vaginal bleeding
· Need or want to avoid estrogen
· Do not want to take contraceptive action daily
Precautions:
· Suspected prenancy
· Undiagnosed vaginal pregnancy
· Breast lumps
· Breast cancer
· Active liver disease(jaundice)
· Beningn or malignanat liver tumours
Instructions for norpalnt implant clients:
· The client should be advised to return to the same clinic where the implants were inserted or to another clinic where the method is provided.The counsellor should be sure that the client knows she has access to removal
· The insertion site will be covered with a band aid and a gauze pressure dressing only no sutures are required
· The area should be kept clean and dry with the pressure dressing in place for 2 days the band aid should be left in place until the incision heals ,about 3-5 days
· The routine work can be done immediately; avoid dumping or straining the implant area for few days.Once healed the area can be touched and washed with the normal pressure.
· If sign of infection occur such as fever, inflammation (redness, plus heat) at the site or if there is persistent pain for several days return to the clinic where the Norplant insertion was done.
Permanent FP methods:
1. Vasectomy:
Vasectomy is the simple operation in which the tubes (vas deferens) that carry the sperm from the testis to the penis are surgically blocked.After this minor procedure the sperm cannot travels beyond the end of the tubes.This operation completes on 10-15 minutes.
Vasectomy is the one of the safest and most efffective method of permanent sterilization with failure rate less tha 1%.The client should use contraceptives for first 20 ejaculations(or for 3 months).Ideally 1 or 2 sperm free semen specimens should be obtained from the man after vasectomy in order to be reasonly sure that the operation was a success.
Indications
· Men of any reproductive (or usually <50)
· Men who have highly effective,permanent contraceptive method
· Men whose wives have age,parity or health problems that might pose a serious health risk if they becomes pregnant
· Men who understand and voluntarily consent to the procedure
· Couples who are certain they have achieved their desired family size
Contraindications :
In clients having;
· Varicocele:Cause bleeding and haematoma after the operation
· Scabies:Infection may spread
· Filariasis:Difficult to operate because the scrotum tissue is thick in filariasis care
· Diabetes:The diabetic client may need special attention and care.By giving local anaesthesia operation is not good for out side operation.
· Coronary heart disease:Operation is not advised if the patient developed coronary heart disease recently
· Hydrocele:Difficult to operate because after the operation there is bleeding
· Atrophic painful testes:The patient throws out the testis if there is atrophic painful testis.So there is need to take advise of the surgeon to do vasectomy.Refer to an appropriate place where there are many facilities
· Beningn or malignant tumours: if the tumours present refer to appropiate place for advice and treatment.
Advantages:
· Minor operation
· Highly effectively
· Doesn’t interfer in intercourse
· Permanent operation ; if done once last long
· No long term side effects
· No change in sexual functions
Disadvantages:
· Permanent:difficult and very expensive to reverse
· May be regretted later
· Delayed effectiveness(requires up to 3 month or 20 ejaculations)
· Risk and side effects of minor surgery especially if general anaesthesia is used
· Doesn’t protect against STI,HBV,HIV and AIDS.
· Doctors are needed for operation
Common side effects:
· Wound infections and haematoma
· Excessive swelling
· Granuloma
· Pain in incisional site
· Sometimes may be mental tension
Preoperative information and instruction to the client:
The preoperative information and instruction are important to ensure the safety of vasectomy and to inform and reassure the client.Health persons should provide all information in the language the client can easily understand.The following points must be explained to all operative clients:
· The steps of the operation
· Instruction for wound care
· What pain and discomfort might occur
· Common post operative complications such as,infections,fever,increasing pain and swelling and what to do in each case and where to go if any complication arises
· The need to use some form of contraceptives for at least 20 ejaculations or for three months,whichever occurs first
· How to use any medication prescribed after surgery
· When to return to work and resume sexual relations
· Health person should orally review each of the above points with all clients
· Preoperative medication and anaesthesia: Usually done under local anaesthesia.however diazepam 5-10 mg may be given to patient 45-60 minutes prior to operation to minimize psychological and emotional distress and feel patient free from pain and discomfort.
· Client should bath and wear clean and loose fitting clothing provided by the surgical facilities
· Ask to bring clean scrotal support cloths
· Pubic haii should be trimmed as it may obstruct the operative area
Post operative care:
Men who have undergone vasectomyand haven’t received sedation may leave the clinic after resting 30 minutes
Before discharging the client, the client should be well instructed about
· Wear a scrotal keep the operative site dry and rest for 2 days
· For pain and swelling take 1 or 2 analgesic tablets(ibrufen or paracetamol)every 4 to 6 hours and apply ice packs
· Stitches are not usually required with no scapel vasectomy:it stitches must be removed,return after 1 week(if absorbable stitches were used to close the skin,there is no need to return unless there are problems)
· Avoid heavy lifting and hard work and cycling for 3 days
· If comfortable,you may resume sexual intercourse in 2 or 3 days
· Remember to use condoms or another F/P method for 3 months or until you have at least 20 times ejaculated
· Should come back for a semen test 3 month after the operation if you wish to have proof that the vasectomy is completely effective.
· The wound needs to be cleaned after 7 days ,keep neosporine powder for quick cure
· Don’t smoke until 1 hour of operation
· Use medicine according to doctor’s prescription
2. Tubal ligation:
The voluntary sterilization process via surgical procedure for permanently termination fertility in women is called tubal ligation.Tubectomy is removing the fallopian tube in females.
Method of tubal ligation:
I. Laproscopy
II. Minilaprotomy
Laproscopy:
The incision was made into the abdomen ,an instrument (the laproscope) is passed into the abdominal cavity and identify the fallopian tubes.Then,tube ligation is performed.The operation is done under general or local anaesthesia.
Minilaprotomy:
The operation is done under local anaesthesia 2-3”incision is done in the lower abdomen .Once the abdomen is opened the fallopian tubes are identifiedusually served by trying up and cutting a small piece of tube,following this the abdomen is closed.A dry sterile dressing is applied and client can be discharged within 2-4 hrs after the procedure.
Time for tubal ligation
· Any time during the menstrual cycle when you can be reasonably sure the client is not pregnant
· During postnatal period tubectomy can be done after 45 days. During this period fallopian tubes can be easily detected.
· For immediate post partum minilaprotomy only should be preformed within 48 hours of delivery
Tube ligation is one of the most effective method of contraceptive with the failure rate usually less
than 1 %(0.4-1% in the first year of minilaprotomy and0.1-0.5% in the first year of laproscopy)
Advantages:
· This operation is easy to do
· Permanent
· Doesnot interfere with the intercourse /no hormone production by ovaries
· It may be used both interval and post partum tubal ligation
· Daily routine work can be done after 7 days
Disadvantages:
· Permanent
· Risk and side effect of sugery
· Doesn’t protect against GTI,other HIV/AIDS,HBV
· Though minor time a scar is seen
Indications for tubal ligation:
· Woman who want highly effective permanent protection against pregnancy
· Woman in whom pregnancy would pose a serious risk
· Woman who are certain that they donot want more children
· Woman who donot want a method that requires daily action or before intercourse
· Woman who understand and voluntarily consent to the procedure
Contraindications:
· Tumours in the abdomen and uterus
· Pregnancy
· Heart disease ,high BP ,anaemia,hernia,diabetes
Common side effects:
· Wound infection
· Pain in the incision site
· Post operative fever(<38°C)
· Bladder,intestine injuries
· Haematoma(subcutaneous)
· Gas embolism resulting from laproscopy(very rare)
· Superficial bleeding(skin edges or subcutaneous)
Preoperative information and instruction to the client:
Pre operative information and instruction are important to ensure the safety of tubal ligation and to inform and reassure the client staff member should provide all information in language the client can easily understand.In postpartum cases , Instructions should be given and after delivery whenever possible.The following points must be explained to all clients
· The steps of the operations
· Types of anaesthesia
· Instruction for care the wound
· What pain and discomfort might occur
· Common postoperative complications(such as infection,fever,increasing pain bleeding and suspected pregnancy) what to do in each case and where to go if complications arises
· How much medication prescribed after surgery
· When to return to work and resume sexual realtions
· Timing of follow up visit
· Staff should orally review each of the above points with the clients
· To prepare for the operation the client should bath if possible and wear clean and loose clothing to the surgical facilty.She should bring someone with her to accompany her home after the operation.
· The client should be told to just 8 hours before surgery.She should be insturcted not to take any medications 24 hours before surgery (unless prescribed by the physician)The night before the surgery she should wash her hair or take a bath if possible.On the morning of the operationshe should her bowel.the client should not wear jewellery,nail polish,or hair pins to the surgical facility.Before entering the operation theater,she should remove eyeglasses,contact lenses dentures and empty her bladder.
Post operative instructions:
· Monitoring vital signs
· Assesment of the wound for soakage and haemorrhage
· Needs to rest for 24 hours after the surgery
· Client can return to normal activities after 3 days of surgery
· Follow up visit should be take place within 7 days or if not possible within 2 weeks of surgery
· Advices on post operative complications and management;
Antibiotics for infection, dressing the wound,analgesic for pain in the operated site and take rest.
Emergency contraception:
Emergency contraception is the contraception provided to women to prevent unintended pregnancy following an un protected act of sexual intercourse.
Its effectiveness is <2% when used correctly
There are two main methods available in Nepal that can be used as emergency contraception .They are
Combined oral contraceptive
A special dosage
§ Low dose 30-33 of mcg Ethyinyl Estradiol(EE) COCs
§ High dose (750 mcg or 0.75 mg Levonorgestral eg.Postinor)
Copper T 380A
Indications for emergency contraceptions
Emergency contraception is only meant to be used following an unprotected act of sexual intercourse to prevent pregnancy.the following situations when a woman can use or may not need to use emergency contraception
· When no contraception method has been used
· In case of contraceptive accident or misuse
v Condom rupture slippage or misuse
v Failed coitus interrupts
v Miscalculation of the periodic abstinence method
v IUD explusion
v Unprotected intercourse prior to the effective time of vasectony
v When the woman has been a victim of sexual abuse e.g. rape
Method
|
Timing
|
Remarks
|
Client’s instruction
|
COCs(The Yuzpe method)
|
Should be taken within 72 hours of unprotected sex and related after 12 hours
|
Effective (2% become pregnant)
Side effects
i.nausea(≤1 day)
ii.vomiting
iii.breast tenderness,headache,dizziness
iv.irregular uterine bleeding,spotting,delayed menstrual cycle
v.if pregnancy is not prevented,counsel client for ANC
|
COCs low dose (30-33ug EE)
Take 4 tablets within 72 hours of unprotected sex
12 hours later
Take 4 tablets.
Total 8 tablets.
|
Progestin only pills(POPs)
|
Should be taken within 72 hours of unprotected sex and repeated after 12 hours
|
Some side effects as with COCs but significantly less severe and nausea /vomitting is minimal.
If pregnancy is not prevented counsel for ANC
|
POP(750mcg or 0.75mg postinor)
Take 1 tablet within 72 hours
12 hours later ,
Take 1 more tablet (Total dose =1500mcgof 1.5mg of levonorgestrel)
POPs(0.75mg norgestrel)
Take 20 tablets within 72 hours
12 hours later,
Take 20 more tablets
Total dose=3mg of norgestrol
|
IUDs
|
Should be inserted within 5 days unprotected intercourse
|
Very effective(<1% pregnant)
i.few side effect
ii.Provide long term contraception as well
Failure increases with longer interval between unprotected intercourse and insertion
*shouldnot be inserted in woman at risk for GIT and other STI
iii. may not be advisable for young nulliparous clients.
|
Counsel client about post insertion bleeding
Help her understand how to distinguish this from a menstrual bleeding.
|